Introduction
Technology is evolving faster than ever. It changes how we work, communicate, and live. As technology trend 2026 approaches, innovations like artificial intelligence, quantum computing, 5G and 6G connectivity, and immersive virtual environments are reshaping industries and daily life. These trends drive efficiency and creativity, but they also challenge businesses, governments, and individuals to adapt quickly.
In the early 2000s, the focus was on connecting people through the internet. The 2010s emphasized mobile and cloud advancements. Now, the 2020s clearly mark the rise of intelligent, autonomous, and sustainable technologies. Artificial intelligence can take independent actions. Quantum computers can solve problems that once seemed impossible. Immersive virtual environments blur the lines between physical and digital spaces. 2026 is set to be a significant year for technological change.
What makes these technology trends especially important is not just their newness but how they come together. Artificial intelligence improves cybersecurity. Advances in connectivity enable the Internet of Behaviors. Sustainable energy solutions combine with AI to reduce waste and improve usage. This interconnected web of technologies forces industries to rethink their models. Governments need to change regulations, and individuals must reassess their skills.
How Technology Shapes Work, Business, and Daily Life in 2026
1. Shaping Work
The workplace is undergoing a significant transformation due to technology. Automation tools and artificial intelligence (AI) handle routine tasks, allowing employees to focus on creative, strategic, and decision-making roles. For example, AI-driven virtual assistants organize calendars, manage emails, and perform data entry.
AI-powered virtual assistants: manage schedules, emails, and data entry.
Intelligent collaboration platforms streamline team communication across time zones.
Virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR): enable immersive training programs, reducing onboarding time and improving skill retention.
Remote and hybrid work models are strengthened by cloud-based platforms and real-time collaboration tools. Workers can contribute to projects from anywhere in the world, increasing productivity and work-life flexibility.
2. Shaping Business
In the business landscape, technology drives efficiency, innovation, and competitive advantage:
Data Analytics & AI: Businesses make smarter, faster decisions by using predictive analytics and AI insights. For example, retail companies can forecast demand and manage inventory dynamically.
Automation & Robotics: Manufacturing and logistics experience cost reductions and faster production through smart factories and AI-driven supply chain management.
Customer Experience: AI chatbots, personalized recommendations, and digital avatars improve customer engagement and satisfaction.
Global Connectivity: 5G and early 6G networks allow businesses to operate seamlessly across borders, accessing markets and talent worldwide.
Startups and traditional companies alike embrace digital transformation to stay relevant, innovate faster, and deliver value efficiently.
3. Shaping Daily Life
Technology is deeply integrated into everyday life and changes how we communicate, learn, entertain, and maintain health:
Smart Devices: Wearables and IoT devices track health metrics, monitor fitness, and optimize home environments.
Digital Assistance: AI assistants help manage schedules, reminders, and personal finances.
Entertainment & Education: XR technologies provide immersive learning experiences and interactive entertainment. For example, students can explore virtual museums or laboratories without leaving home.
Mobility & Connectivity: Advanced transport solutions like autonomous vehicles and smart traffic systems improve commuting and reduce environmental impact.
Technology simplifies routines and creates opportunities for personalization, convenience, and improved decision-making in daily life.
Top Technology Trends of 2026
1. Agentic AI
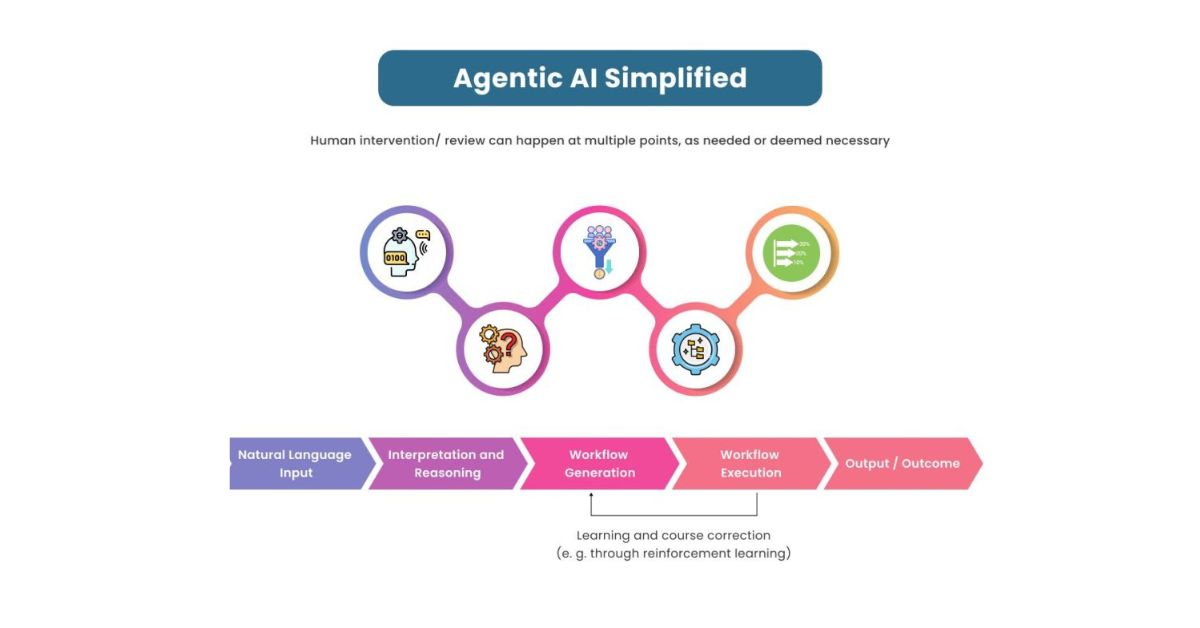
Agentic AI refers to artificial intelligence systems that can act autonomously, make decisions, and pursue goals with minimal human supervision. Unlike traditional AI, which responds to commands, agentic AI can proactively identify problems, plan solutions, and execute tasks in dynamic environments.
Real-world Examples:
-
- Logistics companies use agentic AI to autonomously reroute deliveries in real-time based on traffic and weather conditions.
-
- In finance, agentic AI manages portfolios, executing trades without human intervention while optimizing risk.
-
- Manufacturing plants deploy AI agents to monitor equipment, detect malfunctions, and schedule maintenance automatically.
Benefits:
-
- Efficiency: Automates complex decision-making processes.
-
- Productivity: Frees humans from repetitive or high-stakes monitoring tasks.
-
- Innovation: Enables businesses to experiment with AI-driven strategies faster.
Challenges:
-
- Accountability: Determining responsibility when AI decisions cause errors.
-
- Ethical Concerns: Risk of autonomous systems making biased or unintended choices.
-
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Few laws currently govern fully autonomous AI behavior.
Future Outlook:
Agentic AI is expected to expand across industries, particularly in supply chain management, autonomous vehicles, and smart city operations. Businesses that adopt these systems early could gain significant operational advantages.
2. Generative AI & Multimodal Tools
Generative AI uses machine learning models to create content—text, images, videos, music, and even code—based on data inputs. Multimodal AI combines multiple data types, producing outputs that integrate text, visuals, and sound.
Real-world Examples:
-
- Marketing teams use AI tools to generate personalized ad campaigns combining text, images, and video.
-
- Content creators leverage AI to script videos, design graphics, and even produce synthetic voices for narration.
-
- Developers employ AI to generate functional code, accelerating software development.
Benefits:
-
- Creativity at Scale: Produces high-quality content quickly.
-
- Cost Efficiency: Reduces time and resources required for content creation.
-
- Personalization: Tailors content to user preferences for higher engagement.
Challenges:
-
- Accuracy & Reliability: AI outputs may include errors or hallucinations.
-
- Copyright & Plagiarism Risks: Generated content may unintentionally reproduce existing work.
-
- Ethical Use: Potential misuse for deepfakes or misinformation.
Future Outlook:
Generative AI will increasingly drive personalized media, automated design, and human-AI creative collaboration, but ethical frameworks and AI literacy will be crucial.
3. Quantum Computing
Quantum computing leverages the principles of quantum mechanics to process information exponentially faster than classical computers. It has the potential to solve problems considered impossible for traditional systems.
Real-world Examples:
-
- Pharmaceutical companies use quantum computers for molecular modeling, speeding drug discovery.
-
- Financial institutions run complex risk simulations in seconds instead of days.
-
- Cybersecurity firms test quantum-resistant encryption methods to protect sensitive data.
Benefits:
-
- Unprecedented Speed: Solves highly complex problems rapidly.
-
- Innovation in Research: Enables breakthroughs in chemistry, materials science, and logistics.
-
- Enhanced Security: Facilitates development of quantum-resistant cryptography.
Challenges:
-
- High Cost: Building and maintaining quantum systems is expensive.
-
- Limited Accessibility: Still primarily research-focused; few commercial applications exist.
-
- Technical Complexity: Requires specialized knowledge to operate and program.
Future Outlook:
By 2026, cloud-based quantum computing services will become more accessible to businesses, gradually integrating into industries like pharmaceuticals, energy, and finance.
4. 5G & 6G Connectivity
High-speed connectivity is revolutionizing communication, data transfer, and the Internet of Things (IoT). While 5G is now widely adopted, research on 6G promises ultra-fast, low-latency networks.
Real-world Examples:
-
- Smart cities use 5G to coordinate traffic, reduce congestion, and manage utilities efficiently.
-
- Remote surgeries leverage 5G-enabled robotics for precise, real-time operations.
-
- Autonomous vehicles rely on 5G to exchange data instantly with other vehicles and infrastructure.
Benefits:
-
- Speed & Reliability: Supports real-time applications.
-
- Expanded Iot: Connects more devices with lower latency.
-
- Innovation: Enables AR/VR, smart infrastructure, and AI-driven services.
Challenges:
-
- Infrastructure Costs: Requires large-scale investment to expand coverage.
-
- Security Risks: High connectivity introduces new cybersecurity vulnerabilities.
-
- Global Disparities: Unequal adoption may widen the digital divide.
Future Outlook:
6G networks will enhance immersive experiences, AI integration, and autonomous systems, creating smarter cities and highly connected societies.
5. Spatial Computing (AR/VR/XR)
Spatial computing combines augmented reality (AR), virtual reality (VR), and mixed reality (XR) to create immersive, interactive digital experiences.
Real-world Examples:
-
- Architecture firms use AR to visualize building designs in real-world settings.
-
- Healthcare professionals conduct VR-assisted surgeries and training simulations.
-
- Education platforms employ XR for interactive, immersive learning experiences.
Benefits:
-
- Enhanced Learning & Training: Improves understanding and retention.
-
- Improved Collaboration: Enables virtual teamwork in 3D environments.
-
- Immersive Experiences: Engages users in ways traditional interfaces cannot.
Challenges:
-
- Hardware Costs: Headsets and sensors remain expensive for mass adoption.
-
- Motion Sickness & Accessibility: Prolonged use may cause discomfort.
-
- Content Development Complexity: Creating high-quality XR content is resource-intensive.
Future Outlook:
Spatial computing will expand in enterprise, healthcare, education, and entertainment, gradually becoming part of daily life and professional environments.
6. Internet of Behaviors (IoB) & Edge Computing
IoB collects and analyzes behavioral data to influence decision-making, while edge computing processes data closer to the source for speed and efficiency.
Real-world Examples:
-
- Retailers track shopping patterns to personalize marketing campaigns.
-
- Smart homes adjust lighting, temperature, and security based on user behavior.
-
- Healthcare devices monitor patient behavior to predict health risks.
Benefits:
-
- Personalization: Services adapt to user habits in real time.
-
- Efficiency: Reduces latency and bandwidth issues.
-
- Predictive Insights: Enables proactive decisions in business and healthcare.
Challenges:
-
- Privacy Concerns: Data collection may infringe on user privacy.
-
- Security Risks: IoB systems can be exploited if not properly secured.
-
- Ethical Implications: Behavioral manipulation raises ethical questions.
Future Outlook:
IoB and edge computing will transform retail, healthcare, and smart city management, making systems more responsive and adaptive.
7. AI-driven Cybersecurity & Post-Quantum Encryption
With rising digital threats, AI is now integral to cybersecurity, detecting and mitigating attacks in real time. Post-quantum encryption protects against future quantum hacking.
Real-world Examples:
-
- AI systems detect anomalous network activity and automatically neutralize threats.
-
- Financial institutions implement quantum-resistant algorithms to protect sensitive data.
-
- Governments use AI to monitor critical infrastructure against cyberattacks.
Benefits:
-
- Rapid Threat Detection: Minimizes damage from attacks.
-
- Enhanced Security: Protects against both classical and quantum threats.
-
- Automation: Reduces dependency on manual monitoring.
Challenges:
-
- False Positives: AI systems may misidentify benign activities as threats.
-
- Complex Implementation: Post-quantum encryption requires specialized skills.
-
- Continuous Adaptation: Cyber threats evolve faster than defense mechanisms.
Future Outlook:
AI-driven cybersecurity and post-quantum solutions will become standard across banks, governments, and enterprises, securing sensitive digital assets.
8. Digital Humans & AI Avatars
Digital humans are AI-powered avatars capable of human-like interaction, including voice, gestures, and emotional expression.
Real-world Examples:
-
- Virtual customer service agents provide 24/7 support for businesses.
-
- AI tutors guide students through personalized lessons in real time.
-
- Digital influencers create interactive social media content for marketing campaigns.
Benefits:
-
- 24/7 Availability: Reduces human labor requirements.
-
- Personalization: Adapts interactions based on user behavior.
-
- Scalability: Handles multiple interactions simultaneously.
Challenges:
-
- Ethical Concerns: Risk of manipulation and identity misuse of tech trends.
-
- Realism Limitations: Imperfect human-like behavior may reduce trust.
-
- High Development Costs: Advanced avatars require significant resources.
Future Outlook:
Digital humans will reshape customer support, education, and entertainment, enabling interactive experiences that feel human without human limitations.
9. Wearables & Earables
Wearable devices monitor health, fitness, and environmental factors, while earables (smart earpieces) offer contextual computing and personal assistance.
Real-world Examples:
-
- Smartwatches track heart rate, sleep, and activity.
-
- Earbuds provide real-time language translation and AI-guided personal assistants.
-
- Health devices alert users to irregular heart rhythms or glucose levels.
Benefits:
-
- Health Monitoring: Enables proactive wellness management.
-
- Productivity: Earables assist with reminders, notifications, and contextual tasks.
-
- Convenience: Always-on assistance without needing a phone or computer.
Challenges:
-
- Privacy Concerns: Continuous monitoring collects sensitive personal data.
-
- Battery Life: Limited power may hinder continuous use.
-
- Device Dependency: Overreliance may reduce self-awareness.
Future Outlook:
Wearables and earables will integrate more deeply into healthcare, fitness, workplace productivity, and lifestyle personalization, driving data-driven wellness.
10. Green Technology & Sustainable Innovations
Green tech focuses on sustainable energy, eco-friendly infrastructure, and resource-efficient solutions.
Real-world Examples:
-
- Smart grids optimize energy use and reduce waste.
-
- AI systems manage renewable energy production and distribution.
-
- Electric vehicles (EVs) and carbon-capture technologies lower environmental impact.
Benefits:
-
- Environmental Protection: Reduces carbon emissions and energy consumption.
-
- Cost Savings: Optimizes resource use for businesses and households.
-
- Innovation Opportunities: Opens new markets and jobs in green industries.
Challenges:
-
- High Initial Investment: Green technologies often require significant upfront costs.
-
- Infrastructure Needs: Requires adaptation of existing systems.
-
- Regulatory Complexity: Policies vary across regions, slowing adoption.
Future Outlook:
Sustainable technology trend will become central to corporate strategy, government policy, and daily life, balancing economic growth with ecological responsibility.
Advantages & Disadvantages Technology Trends 2026
The technology trends of 2026 offer significant benefits across industries and daily life. Agentic AI and generative AI boost productivity, automate complex tasks, and enable creative innovation. Quantum computing speeds up problem-solving in medicine, finance, and research. Meanwhile, 5G/6G connectivity and spatial computing improve communication, collaboration, and immersive experiences. IoB and edge computing provide personalized services and faster decision-making. AI-driven cybersecurity protects data against evolving threats. Digital humans, wearables, and earables enhance user interaction, health monitoring, and convenience. Lastly, green technology supports sustainability and energy efficiency, promoting environmental goals.
Conclusion
The technology trends of 2026 are reshaping work, business, and daily life, driving innovation, efficiency, and personalization. While they offer immense opportunities, careful adoption and ethical considerations are essential. Staying informed and adaptable will be key to thriving in this rapidly evolving digital era.
FAQs
1. What is the most impactful tech trend of 2026?
While several technologies are transformative, AI—especially agentic and generative AI—stands out for its ability to automate tasks, enhance creativity, and drive decision-making across industries.
2. Will AI replace human jobs in 2026?
AI will automate certain repetitive or data-driven roles, but it will also create new opportunities in AI development, management, and strategy. Human creativity, judgment, and emotional intelligence remain irreplaceable.
3. How soon will 6G connectivity be available?
6G is still in the research and early development phase, with commercial rollout expected later in the decade. Meanwhile, 5G networks are expanding globally, enabling many high-speed, low-latency applications today.



